2nd Thessalonians
The Hope of Christ's Return
Summary | About | Why You Should Read it | Author | When Written | Context | Timeline | Location | Outline | Observations | Resources
Summary
This epistle provides assurance to the Thessalonians that they have not missed the rapture, as was falsely reported to them in a forged letter, as though from Paul. He then goes on to describe the details of specifically what the rapture entails and what happens immediately thereafter. This makes this letter of utmost importance from an eschatological (end-times prophecy) viewpoint.
The term “rapture” is derived from the Latin “rapturo”, which explains why it is not found in the original text. That text was not written in Latin but in Greek. The term used is “harpazo”, which is translated into English as “caught up”. When translated into Latin, it is “rapturo”.
The table below is a high-level look at the structure and contents of 2nd Thessalonians.
The next table is a high-level look at the structure and contents of x.

About
The second epistle to the Thessalonians is the 14th book of the New Testament and Paul’s 9th book (by biblical order, not chronological order).
Why You Should Read It
Like the first epistle, the primary focus of this letter is on the second coming of Christ, in particular the details about the rapture and the order of events surrounding it. This is most relevant today, as we approach that time. Paul’s explanation of the rapture in this letter help us to understand what to look for regarding the Lord’s return.
Author
Paul is declared to be the author of this epistle (see 1:1 and 3:17). There is more argument as to his authorship than the first epistle, despite support if it being Paul by the early church writers. The disputes relate more to the textual differences and have little support in the theological community. One of the purposes of the letter is to counter other letters that had been forged as though from Paul. He signs off declaring he is signing with his own hand to prove his authenticity. He did this with all 13 of the epistles he wrote.
When Written
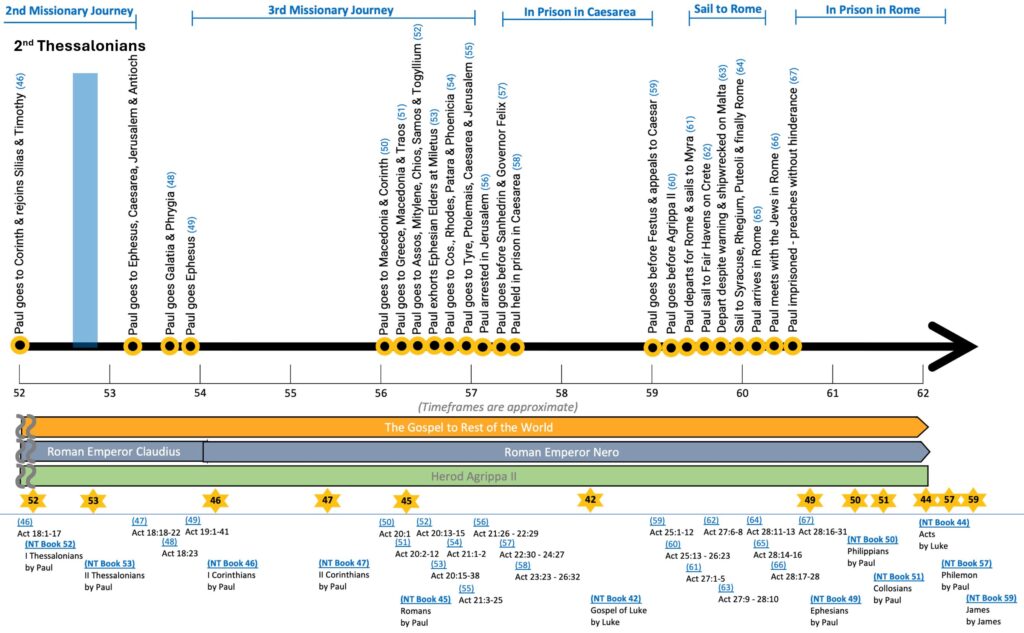
Paul’s second epistle to the Thessalonians was written within a year of his first epistle, around late 52 A.D.
Context
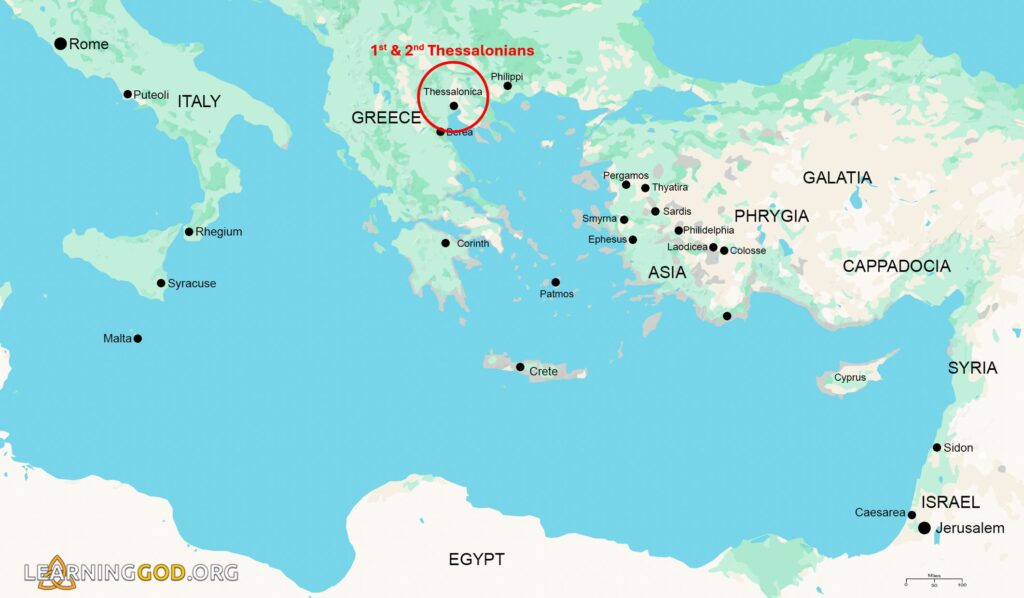
Thessalonica was a bustling seaport city at the head of the Thermaic Gulf. It was an important communication and trade center, located at the junction of the great Egnatian Way and the road leading north to the Danube. It was the largest city in Macedonia and was also the capital of its province.
The background of the Thessalonian church is found in Act 17:1-9. Since Paul began his ministry there in the Jewish synagogue, it is reasonable to assume that the new church included some Jews. However, 1:9-10; Act 17:4 seem to indicate that the church was largely Gentile in membership.
Paul visited Thessalonica on his 2nd missionary journey in 51 A.D. and spent about 3 weeks with them. This letter was written about a year or two later in late 52 A.D. to address fake letters, false reports and missed rapture.
The Jews had recently been expelled from Rome and were causing problems for the Christians in the area.
Timeline
The general order of events from the New Testament period of the early 50s to the early 60s is shown below.
Location
The city of Thessalonica is on coast of Macedonia, in modern day Greece.
Outline
Introduction (ch. 1)
Greetings (1:1-2)
Thanksgiving for Their Faith, Love and Perseverance (1:3-10)
Intercession for Their Spiritual Progress (1:11-12)
Instruction (ch. 2)
Prophecy regarding the Day of the Lord (2:1-12)
Thanksgiving for Their Election and Calling (Their Position) (2:13-15)
Prayer for Their Service and Testimony (Their Practice) (2:16- 17)
Injunctions (ch. 3)
Call to Prayer (3:1-5)
Charge to Discipline the Disorderly and Lazy (3:6-15)
Conclusion, Final Greetings and Benediction (3:16-18)
Observations
- 2 Thessalonians is Paul’s 2nd letter.
- 2 Thessalonians is Paul’s shortest epistle to a congregation.
- NOTE: Philemon is shorter, but it is addressed to an individual.
- Paul uses two words in 2 Thessalonians that are not to be found anywhere else in the New Testament.
- Paul established the congregation at Thessalonica during his 2nd missionary journey, and remained there for about a month.
- Since 1 Thessalonians was written, some false doctrine had been taught in Thessalonica.
- 2 Thessalonians was written to replace error with truth.
- One of his main subjects is again the proper understanding of the Lord’s 2nd coming.
- It is mentioned in 23 of the 27 New Testament books.
- Of 7,959 verses in the New Testament, at least 370 of them refer to the 2nd coming of Christ.
- 1 Out of every 21 verses in the New Testament touches on the subject of the Lord’s return.
- In 2 Thessalonians, Paul also deals with the subject of withdrawing fellowship from the disorderly. 3:6-15
- In Paul’s salutation to the brethren at Thessalonica:
- He uses the customary Greek, “grace.”
- He uses the customary Hebrew, “peace.”
- The city of Thessalonica.
- Capital of the Roman province of Macedonia.
- A prominent seaport city.
- Situated on the great northern military highway from Rome to the east.
- Located 100 miles west of Philippi.
“But as for you, brethren, do not grow weary in doing good.”
2 Thessalonians 3:13
Sections in II Thessalonians
- Affirmation amidst affliction 1
- Explanation of prophecy 2
- Clarification regarding response 3
Theme
- The hope of Christ’s return encourages us in our suffering and motivates us to live responsibly for Him.
- This epistle was written to correct the false understanding that the people of the time had missed the rapture. Paul explained what to look for when the time comes.
Jesus in II Thessalonians
- Jesus is the coming Judge who will reward the righteous and destroy the wicked, including the coming man of lawlessness in the end times (1:6-2:12).